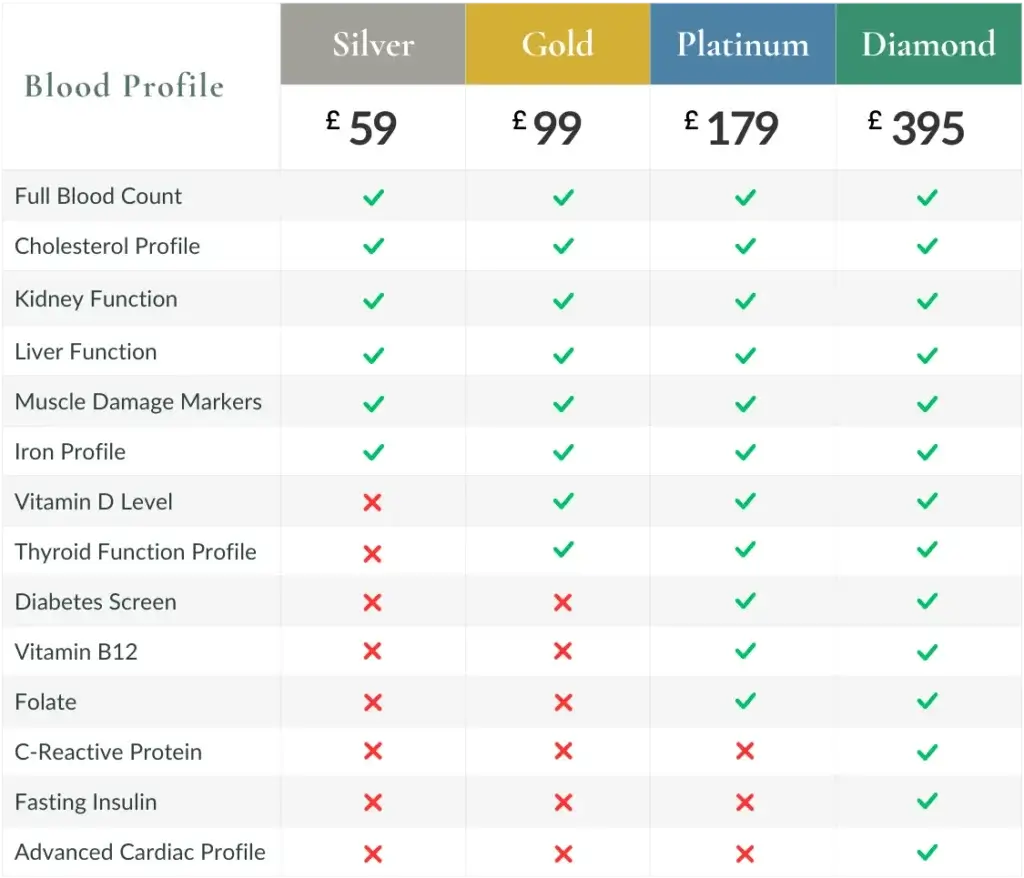
Our Diamond blood profile, with 59 biomarkers, gives you a crystal ball into the future. It includes informative and specialist cardiac risk markers, fasting insulin, and inflammatory markers. These markers will help you understand the future risks to your health that you may be predisposed to, including diabetes, heart attacks, and strokes.
This profile is perfect for anyone who has a family history of cardiovascular diseases and stroke or wants to know their future risk to manage it effectively.
Here are some of the exceptional biomarkers in the Diamond Profile and why they are helpful:
Recent research has illuminated the significance of various biomarkers in predicting risk and guiding therapeutic interventions. Testing for apolipoproteins, lipoproteins, and inflammatory markers has gained prominence in the evolving landscape of cardiovascular health.
Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) & Apolipoprotein B (ApoB)
Apolipoprotein A1 is a major component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), often referred to as “good cholesterol.” Recent studies indicate that higher levels of ApoA1 are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Thus, it is a valuable marker for assessing cardiovascular health and the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions.
Conversely, Apolipoprotein B is a key component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), which are linked to atherosclerosis (thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a build-up of plaque in the inner lining of an artery).
Elevated levels of ApoB correlate with an increased risk of heart disease, providing a more accurate risk assessment than traditional cholesterol measurements. The ApoB/ApoA1 ratio is emerging as a powerful indicator of cardiovascular risk, highlighting the balance between “good” and “bad” cholesterol.
Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)]
Lipoprotein (a) is a unique lipoprotein with genetic determinants. It is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Recent research has emphasized the importance of measuring Lp(a) levels, especially in individuals with a family history of heart disease or those with unexplained cardiovascular events.
High Lp(a) levels are linked to increased inflammation and potential thrombosis, making it a critical marker in personalised cardiovascular risk assessments.
Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2)
Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2 is an enzyme involved in the inflammation process associated with atherosclerosis. Elevated levels of Lp-PLA2 are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Recent studies suggest that measuring Lp-PLA2 can help identify individuals at a higher risk of heart disease, even when traditional lipid profiles appear normal. Thus, this biomarker may be a valuable addition to risk stratification tools.
HS C-reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a marker of systemic inflammation. Research has demonstrated that elevated hs-CRP levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, independent of traditional risk factors.
Regular testing of hs-CRP can be beneficial for the early identification of individuals at risk, allowing for timely intervention through lifestyle modification or pharmacotherapy.
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen is a protein involved in blood clot formation and is another marker of inflammation. Elevated fibrinogen levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Recent studies indicate that measuring fibrinogen can provide additional insights into an individual’s cardiovascular risk, especially in conjunction with other inflammatory markers. It can also serve as a target for therapeutic intervention in high-risk patients.
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is an amino acid that, when elevated, has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Recent research suggests high homocysteine levels can damage blood vessels and promote thrombosis.
Testing for homocysteine can be particularly beneficial in individuals with a family history of heart disease or those with other risk factors, guiding dietary and supplementation strategies to manage levels effectively.
Fasting Insulin
Fasting insulin levels are crucial for assessing insulin sensitivity and the risk of metabolic syndrome. Elevated fasting insulin can indicate insulin resistance, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Recent studies highlight the importance of fasting insulin testing in identifying individuals at risk and implementing early lifestyle changes or pharmacological interventions to mitigate these risks.
Armed with this information, you can make informed choices about your lifestyle and health habits, consider additional testing and screening or seek a full cardiological review, where your risk factors are elevated, empowering you to stay healthy and catch the disease before it develops.
To book your Diamond profile, call us today or book online!
Blood Test Packages
What to expect
Requirements & preparation
Procedure
Results
💾 Download The Sample Report